Positive Outlook for Cyprus Economy
In a recent announcement, Capital Intelligence Ratings (CI Ratings) has revised its long-term foreign currency rating (LT FCR) outlook for the Republic of Cyprus from stable to positive. This revision comes alongside the affirmation of the country’s LT FCR and short-term FCR (ST FCR) at BBB- and A3 respectively, signaling confidence in the nation’s economic trajectory.
The upgrade in outlook is attributed to a faster-than-anticipated reduction in government debt, credited to consistent primary fiscal surpluses and proactive debt management. CI Ratings highlighted the government’s efforts in managing its debt maturity profile effectively, which has reduced refinancing risks and increased cash buffers to counteract short-term shocks and external vulnerabilities.
Significant progress in resolving non-performing loans (NPLs) within the banking system has also contributed to the positive outlook. This has led to a considerable decrease in the state’s contingent liabilities from the banking sector. Despite a challenging external environment and restrictive global financial conditions, fiscal risks are currently deemed manageable.
The agency also recognized Cyprus’ economic resilience, high per capita GDP, and the benefits of EU and eurozone membership, which includes access to financial support through the Recovery and Resilience Facility (RRF). The general government debt-to-GDP ratio saw a decline to 77.3 per cent in 2023 from 85.6 per cent in 2022, reflecting a higher-than-forecast primary budget surplus and repayment of bonds and loans.
CI Ratings anticipates that the dynamic of public debt will remain favorable, with a projected decline in the debt-to-GDP ratio to 66.2 per cent by 2025. The government’s budget performances remained strong in 2023, with an overall surplus recorded at 2.9 per cent of GDP. The general government budget is expected to maintain a surplus averaging 3.1 per cent of GDP through 2024-25.
However, risks to Cyprus’ fiscal outlook persist, including potential increases in expenditures on subsidies, social welfare, and public sector wages. Other risks to the budget include costs associated with the national healthcare system (Gesy) and possible declines in tax revenues if GDP growth faces downward pressures.
The impact of high-risk premiums and strict eurozone monetary policy on public finances is considered manageable, thanks to a reduction in general government debt and a high proportion of debt at fixed interest rates. Short-term refinancing risks have remained stable due to sound fiscal management and prudent creation of cash reserves.
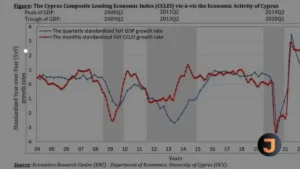
Despite external adversities, economic growth remains positive with real GDP estimated at 2.5 per cent in 2023. Key sectors such as hospitality, construction, wholesale and retail trade, as well as information technology, have shown restrained growth.
The strength of the banking sector has improved with the total non-performing loan (NPL) ratio decreasing to 8.3 per cent of total loans. The capital adequacy of the banking sector is healthy, with a CET-1 ratio averaging 21.4 per cent at the end of September 2023.
Cypriot banks have made significant progress in deleveraging, with the banking sector’s assets-to-GDP ratio decreasing. Looking ahead, CI Ratings expects real GDP to increase by an average of 2.6 per cent in 2024-25, supported by improved domestic demand and continued investment.
The agency also notes that the rating could be upgraded if the government implements comprehensive structural reforms leading to improved revenue mobilisation and faster resolution of legacy NPLs. Conversely, the outlook could be revised to stable if fiscal performances weaken or if adverse shocks lead to deterioration in public or external finances.