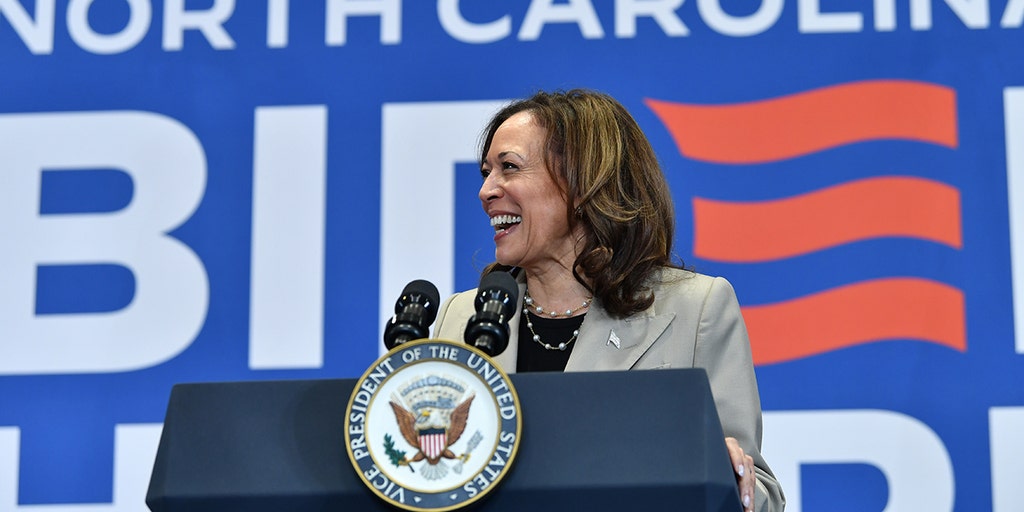
Vice President Kamala Harris holds a campaign event in Fayetteville, North Carolina on July 18, 2024. (Photo by Peter Zay/Anadolu via Getty Images / Getty Images) Here’s a closer look at where the vice president stands on key economic issues, should she win the party’s nomination.
Taxes
The coming election is particularly consequential because whichever party voters select to control the White House and Congress next year will determine the fate of the Tax Cuts and Jobs Act. Enacted in 2017 by Republican lawmakers and Trump, the law drastically overhauled the nation’s tax code, including reducing the top individual income tax bracket to 37% from 39.6% and nearly doubling the size of the standard deduction. However, those changes to the individual section of the tax code are poised to sunset in 2025, meaning that many taxpayers – including those who earn less than $400,000 – will face steeper levies if the law is not extended. More than $3.4 trillion in individual income and estate tax cuts are set to expire next year if Congress does not act.
As a presidential candidate in 2019, Harris proposed replacing the tax law with a monthly refundable tax credit worth up to $500 for families earning less than $100,000. The credit would begin to phase out for individuals earning more than $50,000. Harris also called for raising the corporate tax rate to 35% and taxing capital gains at regular income rates.
Student Loans
While running her presidential campaign, Harris touted a student-debt forgiveness plan as part of a broader proposal to invest in Historically Black Colleges and Universities and Black entrepreneurs. Under Harris’s plan, borrowers who received a Pell Grant could have up to $20,000 of their student loans forgiven if they start a business and operate it for at least three years in a disadvantaged community.
Harris later endorsed Biden’s proposal to cancel up to $10,000 of federal student loans per borrower. The Supreme Court struck down that attempt one year ago, although Biden is trying again.
Health Care
Harris introduced a plan in 2018 to achieve universal health care coverage by expanding Medicare with the help of private insurers. “Medicare works,” Harris wrote in a Medium essay at the time. “Now, let’s expand it to all Americans and give everyone access to comprehensive health care.”
In order to pay for the expansion, Harris pitched several new taxes on financial trades, including taxing stock trades at 0.2%, bond trades at 0.1% and derivative transactions at 0.002%. She claimed it would raise “well over $2 trillion” within 10 years.
Lease and Economic Policies
Understanding what is a lease and its implications can provide insights into economic policies proposed by political figures like Harris. The lease meaning involves a contractual agreement where one party grants another party the right to use an asset for a specified period in exchange for payment. This lease definition is crucial when considering policies related to housing and business operations.
Harris’s economic policies, such as capping national rent increases and supporting small businesses through student loan forgiveness, can be seen as efforts to make leasing more affordable and accessible. By addressing these issues, Harris aims to create a more equitable economic environment where leases play a vital role in both personal and business finances.